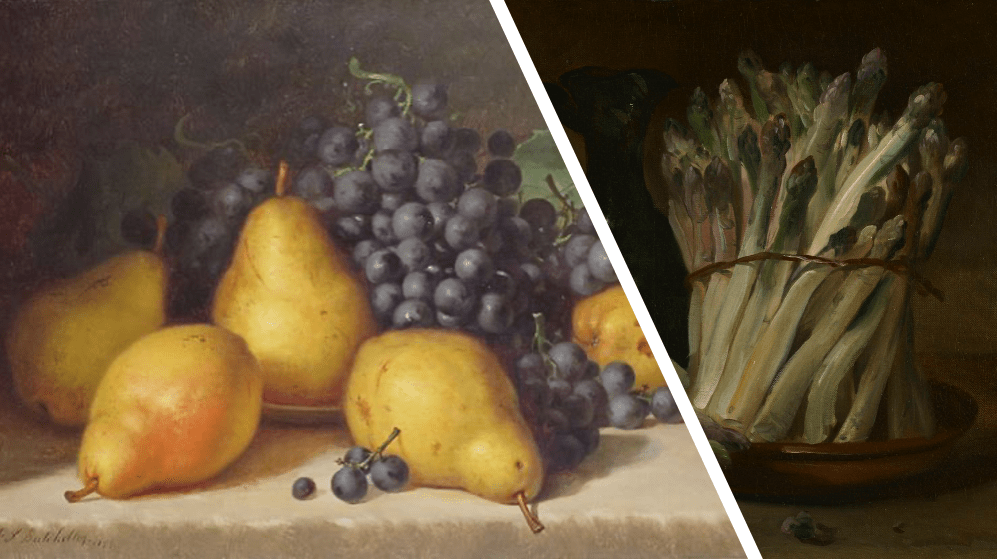This entry is part of a series called “The Gospel in a Postmodern World.” Learn more about the series here.
Preached on November 6, 2022
Scriptures: Psalm 51, Romans 3:9-20
This is sermon three in our series on the Gospel in a postmodern world. In our first week, we talked a little about the current state of things in the West. Statistically, Christians are more likely to lose their faith than in any prior generation and conversions are rarer than ever before. Rather than assume that it’s just a product of every church being incompetent or suggesting that the Gospel needs a hip new revision for a new era, I went in a different direction. I suggested that the current Western cultural movement, Postmodernism, is one that is especially challenging for Christianity to flourish in. The doctrinal orthodoxy of pop-culture is not kind to our faith. We can’t just keep doing the same old same old. We have to accept that we are missionaries in this new world, and the first step for any missionary is to evaluate the culture. Know it. Know the advantages and the disadvantages. Know the challenges and the easy moves. Know what people expect. Then you can go from there.
In week two, we talked about truth. The postmodern world is typified as a post-truth world. There is no popular framework for real, objective truth. There’s only subjective truth. What’s true for me is not what’s true for you. Truth is little more than an opinion that’s accepted by all present. This will not do. Christianity, from its inception, claimed to be genuinely true, not partially true or a truth in a competing market of reasonable truth claims. Christians have to be people concerned with OBJECTIVE truth, calling people back to a genuine reality that was created by God.
And then we had a slight departure from the series in Reformation Day. Which was fun! I love doing a little history. We talked about Martin Luther and the origins of Protestantism. We learned about sola Scriptura and sola fide. And near the end of the sermon, I mentioned that works righteousness was making a comeback. People today, if they assume a god exists, don’t see themselves as someone who needs salvation from the God in question. All in all, they don’t tend to see themselves as something that needs saving. Which makes sharing the gospel in a traditional way a challenge. “Hey, did you know God will forgive all your sins in Jesus Christ?” “What sins?” “The ones you’ve done your whole life long!” “That’s pretty presumptuous of you. I haven’t really done any sins that matter. Actually, I’m one of the good ones. Shame on you for being so judgy.”
And some of you may feel as though that’s an untrue statement. You might think, “Hey, most people would agree to their sinfulness on some level, Vincent. You’re just being judgy.” So let me clarify my observation here: how many people that you meet genuinely consider the core of their humanity to be tainted by original sin? How many people genuinely think that they’re only capable of good by God’s grace, without which they are only able to sin? Not a lot. The average assumption about human nature isn’t that it’s hopelessly flawed. It’s that it’s actually shockingly good. Let’s think about a pop culture example that states this theory pretty clearly.
How many of you saw The Greatest Showman? It came out about 5 years ago. It was actually up for a few awards, if I remember correctly. It’s this musical about the circus. In that movie, there’s a group of people that belong to the circus’s freak show. They’ve had hard lives. They’ve been made fun of. They’ve been ostracized. But now? Now that they’re in a community together, they’ve gained the confidence to be themselves… and they sing this power ballad: This is Me.
I am not a stranger to the dark
Hide away, they say
‘Cause we don’t want your broken parts
I’ve learned to be ashamed of all my scars
Run away, they say
No one’ll love you as you are
But I won’t let them break me down to dust
I know that there’s a place for us
For we are glorious
When the sharpest words wanna cut me down
I’m gonna send a flood, gonna drown ’em out
I am brave, I am bruised
I am who I’m meant to be, this is me
Look out ’cause here I come
And I’m marching on to the beat I drum
I’m not scared to be seen
I make no apologies, this is me.
What is the assumption about our singers? That deep down, they’re incredibly beautiful. They’re different in a way that scares the world, and so the world has tried to keep them down. So they have to band together and resist the pull of society! They have to learn to be authentically themselves in a hostile world.
The problem isn’t with me! The problem is OUT THERE in society!
Now, obviously in that example, it’s hard not to agree. Being mean to a bearded lady because they look different is unambiguously cruel. But that ballad spoke to people from every walk of life. It won the Golden Globe award for the Best Original Song, it was nominated for an academy award and a Tony, and it had millions of replays on every music streaming service you can think of. And why? Because it’s easy to relate. It’s easy to feel like someone who is uniquely beautiful that’s being held back by society. That’s part of the philosophical lens of the postmodern world. Sin isn’t something in me. I’m pretty amazing once you get to know me. SOCIETY is the sinful thing. If you tell me Im sinful, that’s not gonna resonate. It’s mean. I’m pretty good. If you tell me society is sinful… oh, man. AGREED. Society IS dreadful. We need to get rid of that thing so that I can start being my authentic self!
The orthodox Christian view is very different than the modern Western view. And just to drive that point home, I want to look at two philosophers. One a very orthodox Christian theologian. One a philosopher of the Enlightenment. Both men wrote a book named Confessions. Both of those books detail a story in which they stole produce. But the takeaway for each man is totally different depending on how they think about sin and what needs redemption.
Our orthodox Christian is Augustine of Hippo. In his Confessions (written sometime in the fourth century) when he was a teenager, he was hanging out with his friends one night… and they saw this tree of pears on someone else’s property. And what did they do? They stole the pears! They snuck into the yard, filled a basket with the pears, and made off with them. Why? Not to eat them. As a matter of fact, they had better pears at home. They just threw the basket of pears to some pigs and laughed about the whole thing. No, they stole them because it wasn’t allowed. They wanted to break the rules. They wanted to steal. They wanted to destroy something beautiful! He writes:
“It was foul, and I loved it. I loved my own undoing. I loved my error–not that for which I erred but the error itself. A depraved soul, falling away from security in thee to destruction in itself, seeking nothing from the shameful deed but shame itself.”
-Augustine, Confessions
For Augustine, why did he destroy the pears? Because something is wrong INSIDE. There’s something deadly wrong. That’s why we need salvation… because from our birth, something inside is veering us away from life towards death. That’s sin. That’s the problem. Original sin was something humans were born with. Because of humanity’s fall when Adam and Eve ate that fruit that God told them not to, humanity’s nature itself was changed. We went from law-abiding creatures to law-breaking creatures. So every one of us, regardless of what we’ve done specifically, is tainted by original sin.
Now, let’s move to Rousseau. Rousseau was a philosopher in the Enlightenment and he ALSO wrote a book called Confessions. Make no mistake, if you’re a nerd, you don’t accidentally write a book called Confessions without knowing what you’re doing. He’s deliberately drawing his audience’s attention to Augustine. And he ALSO includes a story about produce theft with friends! But notice how he tweaked things. He’s working for this guy whose mother has a little garden growing nearby. And this boss asks him to regularly go steal a little bit of asparagus from that garden, sell the asparagus, and give him the proceeds. He’s really uncomfortable that he would be asked to do this by an authority, but he wants to please the boss, so he does it. And after a few times, he starts to become bitter. He asks himself a question: “Why am I taking on all the risk with none of the reward?” So he starts skimming a little off the top. But that’s not really enough to make it worth the punishment that he would endure if he were caught stealing, so he starts stealing other little things that he finds around the house. Apples. Trinkets. Anything that he can get his hands on. He’s been put in an unjust situation! In his mind, additional theft at least gives him what he’s owed for his boss’s unfair demands. Notice what slowly twisted him. Was it his inner desires? No! The real culprit was society! He writes:
A continual repetition of ill treatment rendered me callous; it seemed a kind of composition for my crimes, which authorized me to continue them, and, instead of looking back at the punishment, I looked forward to revenge. Being beat like a slave, I judged I had a right to all the vices of one.
-Jean-Jaques Rousseau, Confessions
Rousseau doesn’t believe in original sin like Augustine does. He believes in what I’ll call “the beauty of authenticity.” He thinks people are fundamentally good. The thing that causes trouble is society. Society warps people. It makes them want to be other than what they are. They start to try to be better than. Bigger than. Smarter than. They want to be the boss! And for them to be better than, others have to be lesser than. People, fundamentally good, are warped by the society around them. People have to learn to let go of society’s corrupting grasp and be the beautiful creatures they always were.
Pears and asparagus. Both stolen. Both thefts encouraged by friends. But the locus of conversion is very different. Do we need to convert individual people? Or do we need to convert society?
And some of you, I’m sure, are saying, “Vincent, slow down. Aren’t they both right? Isn’t it true that society needs changing and people need changing?” Sure. But what we’re trying to identify is the root problem. If it’s society, I can set out to create bulwarks against unrealistic expectations and oppressive forces to recover the goodness that each person secretly holds in their hearts. It’s not going to be easy, but it’s doable. If the problem is that original sin has corrupted human hearts… well that’s a bigger challenge that we can tackle. That’s when we need to get someone much bigger involved.
The seeds that Rousseau planted during the Enlightenment took root. And they grew. And today we see their expression in movies like The Greatest Showman. People are wired to critique the world around them. Ask anyone! Ask, “What cultural forces are preventing you from being yourself?” You’ll get a laundry list of answers. Easy. Ask someone, “What sins are preventing you from being yourself?” and you’ll get a less warm answer. Similarly, it’s really hard to talk to someone about a God that forgives their sins when people aren’t really concerned about their own sins. It’s much easier to talk about a God that wants to change the world around me.
And I include myself in that. Remember, as we critique culture, we’re a part of it. We don’t get to say, “This is what other people do!” No, this is what WE do too. It’s really hard to talk about personal sin, it’s easy to talk about societal sin. That isn’t a natural human instinct to push the blame onto someone else. It’s a cultural shift. The early Methodists were required to be in small groups. You couldn’t be a Methodist without being in a small group. It didn’t work that way. And during your small group, you had confession time. With everyone there. And you named every sin that you were wrestling with. And everyone there prayed for God to help you with those sins. Can you imagine doing that today? No way! That sounds insane! Give me a justice group or something. Let me go solve the problem OUT THERE! But the problem in here? Psht. Get that outta here. It’s good enough.
So let’s think about this shift. Can Christianity let go of its commitment to original sin and shift to focus primarily on societal sin? No. No we can’t. That’s not to say we can’t acknowledge that there’s sin out there. It’s not to say that we can’t work to try to help those affected by it. But we can’t say, “people are fundamentally good and we just need to work on some really good laws until we get it just right and THEN everything will be good.” We can’t. The problem is deeper than that. According to the Bible, we could come up with the most perfect society in the world, all the best laws, totally remove all oppressive forces, totally remove all need to feel better than or worse than… and we’d still manage to mess it up.
Turn in your Bible to Romans 3 verse 9:
What shall we conclude then? Do we have any advantage? Not at all! For we have already made the charge that Jews and Gentiles alike are all under the power of sin. As it is written:
“There is no one righteous, not even one;
there is no one who understands;
there is no one who seeks God.
All have turned away,
they have together become worthless;
there is no one who does good,
not even one.”
“Their throats are open graves;
their tongues practice deceit.”
“The poison of vipers is on their lips.”
“Their mouths are full of cursing and bitterness.”
“Their feet are swift to shed blood;
ruin and misery mark their ways,
and the way of peace they do not know.”
“There is no fear of God before their eyes.”
Now we know that whatever the law says, it says to those who are under the law, so that every mouth may be silenced and the whole world held accountable to God. Therefore no one will be declared righteous in God’s sight by the works of the law; rather, through the law we become conscious of our sin.
Most of what we have in this section is just Paul quoting other parts of the Bible. He’s quoting several different psalms and Isaiah. Why? To talk about our sin. And is this because Paul hates people? Not at all. He thinks that people have a problem that’s deeper than societal pressures. He thinks our hearts are fundamentally infected. And if you have an infection in your heart, do you worry about polishing up your social interactions? Do you say, “Man, I just try harder and the infection will just go away!” No. You don’t solve an infection with willpower. You call a doctor. Paul is trying to tell us that there’s this infection in our hearts. And he knows the doctor: Jesus.
What shall we conclude then? Do we have any advantage? Not at all! For we have already made the charge that Jews and Gentiles alike are all under the power of sin
What’s going on here? Paul is addressing whether or not Jews have an advantage over Gentiles in regard to sin. After all, they had the law, right? Surely someone who knows the law will be in less trouble than someone who doesn’t have the law! They’ve got everything right there! You might think about this as though it’s about church people today. Don’t we have an advantage against sinning? We’ve got the Bible! We’ve got church tradition! But what does Paul say? NO! You’re not any better off! You’re a sinner. You’ve got the same infection that they’ve got. You need a doctor just as bad. Sin isn’t just a problem that requires some better laws. It’s deeper than that. You need something bigger.
And now Paul gives us that big list of Scripture quotes:
“There is no one righteous, not even one;
there is no one who understands;
there is no one who seeks God.
All have turned away,
they have together become worthless;
there is no one who does good,
not even one.”
“Their throats are open graves;
their tongues practice deceit.”
“The poison of vipers is on their lips.”
“Their mouths are full of cursing and bitterness.”
“Their feet are swift to shed blood;
ruin and misery mark their ways,
and the way of peace they do not know.”
“There is no fear of God before their eyes.”
Look at what he’s doing here. He’s naming all of humanity first off. Little babies. Old folks. Everyone. Nobody is righteous. Not one. All have turned away. And now he goes all throughout the human body to show just how lost we are. Our throats. Our tongues. Our mouths. Our feet. From head to toe: infected by sin.
And every so often, there’s someone who gets tripped up by that word “fear.” Fear of God means respect in this context. Don’t get tripped up. It’s reverence in the face of his awesome majesty. It’s the sobering recognition that he’s in charge of every aspect of everything ever. It’s that feeling of proper smallness in the face of infinite bigness. It’s not fear that he’ll hurt you. That’s not what Paul is trying to say. He’s saying, nobody has a right relationship with God. Not one of us.
Now we know that whatever the law says, it says to those who are under the law, so that every mouth may be silenced and the whole world held accountable to God. Therefore no one will be declared righteous in God’s sight by the works of the law; rather, through the law we become conscious of our sin.
The problem should be clear at this point. It’s not JUST what’s outside. Sure that’s wrong. But more than that, there’s a problem inside. Let’s read on to see the solution.
But now apart from the law the righteousness of God has been made known, to which the Law and the Prophets testify. This righteousness is given through faith in Jesus Christ to all who believe.There is no difference between Jew and Gentile, for all have sinned and fall short of the glory of God, and all are justified freely by his grace through the redemption that came by Christ Jesus.
There’s the solution. Faith in Christ is the only thing that can cure us. Our works aren’t enough. Just like with Martin Luther last week, you can try and try and try and no amount of effort will ever be enough to solve the problem. Every person on earth is redeemed not by works, but by faith. A commentator named Handley Moule writes: “The harlot, the liar, the murderer, are short of it; but so are you. Perhaps they stand at the bottom of a mine, and you on the crest of an Alp; but you are as little able to touch the stars as they.” Everyone falls short, but everyone can be justified freely by His grace. The doctrine of original sin matters because you can’t cure a disease that you don’t know about. If we say we’re all good inside and it’s just a matter of outer troubles, we’re addressing the wrong problem.
But what do we do if maintaining sinfulness is a part of the core Christian thing? How do we evangelize to people who don’t see themselves as sinful? If you don’t need to be saved, how can I introduce a savior? I spoke with a campus minister from the university recently, and he actually brought this up. He mentioned that evangelizing to people by talking about their sinfulness and need for a savior might have worked 50 or 60 years ago, but today, it’s just a non-starter. People don’t recognize their personal sin or need for a savior. But something that has proven to be especially effective is evangelism about relationship. We live in a timeframe where people are more isolated than ever. In Robert Putnam’s landmark study, Bowling Alone, one of the metrics he used to check societal isolation was the size of groups that people went bowling in. Now, people go bowling by themselves more than ever. Bowling leagues are much smaller than they were in the past. And that’s just the metric he chose as his central conversation piece for the book. Social clubs are dying in droves, petitions are less common than ever, people know their neighbors less, people meet their friends more rarely. Community is at an all time low. People are lonely. This campus minister recognized that and used it to evangelize. He talked to people about how God wants to be in relationship with them, despite all the ways they’ve been pushing him away. THAT worked. THAT was effective at opening a conversation about God.
People may not feel guilty, but they feel alone. They know that something is wrong in this world and they’re desperately trying to fix it. Do they need to know about sin? Yes. Absolutely. But leading with that isn’t going to make sense. It’s going to feel like an attack and people will defend against an attack. Guilt versus innocence may not make sense, but loneliness and closeness do. It’s not a perfect substitute. After all, if I’ve hurt God, can’t I do something to make it better? There’s that gap where it’s not completely addressing the sin problem. But, you know, it’s not works-centric and it’s still accurate. Sin is a doctrine that will probably take some time for people to understand in our era. That’s ok. Not everything will make sense all at once. Sometimes, you just need to get a foot in the door and see where things go. When I was first Christian, I barely had anything that looked like a genuine Christian faith. The only doctrines I thought seemed good were Heaven and a good God. The rest just seemed crazy! But the deeper doctrines need more time to teach. I was hooked by the lure of eternity and and God pulled me in from there.
As we evangelize today, it’s important to recognize that people won’t see themselves as sinful. This is a hard doctrine. And unlike objective truth, a debate won’t gain us any ground. But we can pivot. We can acknowledge that we are far from God. Our relationship is weak. Only through Christ’s sacrifice can we approach God afresh. And when people start to encounter God, they’ll recognize that it’s not enough to just say hi. Something more is necessary. Something that transforms what they are into what they were always supposed to be. And it’s a good reminder for us too. When we don’t feel particularly sinful. When we’re convinced that we’re just a good person trapped in crummy circumstances that someone else really ought to clean up… well that’s when we need to recognize that our relationship with God is weak. If we’re blaming the world as though he doesn’t know what’s going on in it, we need to spend some time with him. Only then will we start to see the transformation that we need.
Amen.